Finding the best shoes for bunions isn’t just about comfort — it’s about protecting your feet from further pain and long-term damage. Bunions, those bony bumps at the base of the big toe, can make everyday shoes feel like torture if they don’t fit properly. The right footwear can ease pressure, reduce irritation, and help you stay active without constant discomfort. In this guide, we’ll explore what causes bunions, the symptoms to watch for, and the shoe features that make all the difference.
For a full overview of how toe pain connects to wider foot strain, explore our Complete Guide to Foot Pain Relief.
💡 Quick Answers Available
Want to know more about the best shoes for bunions and how to ease the pain? Scroll down for 20 quick Q&As.
What Are Bunions?
A bunion is a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. Over time, the big toe shifts inward, forcing the joint outward. This can cause swelling, tenderness, and sharp or aching pain — especially when wearing shoes that are too tight in the toe box.
Bunions may develop slowly over years and often run in families. Left untreated, they can worsen, making it difficult to walk comfortably.
Causes of Bunions
- Genetics: Inherited foot shape and mechanics.
- Footwear: Narrow or pointed shoes that crowd the toes.
- Flat Feet & Low Arches: Can increase bunion risk.
- Medical Conditions: Arthritis or connective tissue disorders.
- Injury: Damage to the toe joint can accelerate changes.
Symptoms of Bunions
- A visible bump at the base of the big toe.
- Pain, redness, or swelling around the joint.
- Restricted movement of the big toe.
- Corns or calluses caused by overlapping toes.
- Difficulty finding comfortable footwear.
If your toes have started curling or overlapping, read how the right shoe design can help prevent hammer toes from forming.
Why the Right Shoes Matter for Bunions
Poorly fitting shoes can make bunion pain unbearable. The best shoes for bunions reduce pressure, allow space for swelling, and keep your foot stable. Wearing supportive footwear won’t reverse a bunion, but it can:
- Reduce daily pain and discomfort.
- Prevent further misalignment.
- Lower the risk of corns, calluses, or blisters.
- Help maintain better mobility.
Friction from bunion pressure often leads to corns and calluses — here’s how to manage them and prevent future irritation.
What Are the Best Shoes for Bunions?
Look for these key features:
- Wide Toe Box: Space for toes to spread naturally without rubbing.
- Soft Uppers: Stretchy materials like mesh, soft leather, or knit that move with your foot.
- Low Heels: Flat or low-heeled shoes reduce pressure on the forefoot.
- Cushioned Insoles: Shock absorption for comfort during walking.
- Adjustable Fastenings: Laces, straps, or Velcro for a flexible, personalised fit.
- Removable Insoles: Makes room for orthotics if needed.
✨ Tip: Stylish wide-fit shoes now exist — so you don’t have to sacrifice looks for comfort.
Treatment & Relief Options
At-Home Care
- Wear wide, cushioned shoes.
- Use bunion pads or gel shields to reduce friction.
- Apply ice packs to reduce swelling after activity.
- Try toe spacers for temporary alignment relief.
Professional Care
- Surgery is reserved for persistent, painful cases.
- Custom orthotics can improve foot mechanics.
- Physiotherapy exercises may reduce strain.
- Corticosteroid injections may help severe inflammation.
Prevention Tips
- Avoid narrow, pointed shoes.
- Choose footwear with extra depth and width.
- Keep a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Stretch and strengthen feet daily.
- Replace worn shoes regularly.
When to See a Doctor or Podiatrist
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- Persistent bunion pain despite footwear changes.
- Severe swelling, redness, or infection signs.
- Rapidly worsening deformity.
The Bigger Picture: UK Prevalence
Bunions are extremely common in the UK, especially in women over 65.
- Women are several times more likely than men to develop bunions.
- Prevalence rises sharply with age.
Here is a detailed pie chart showing the prevalence of Bunions in the UK
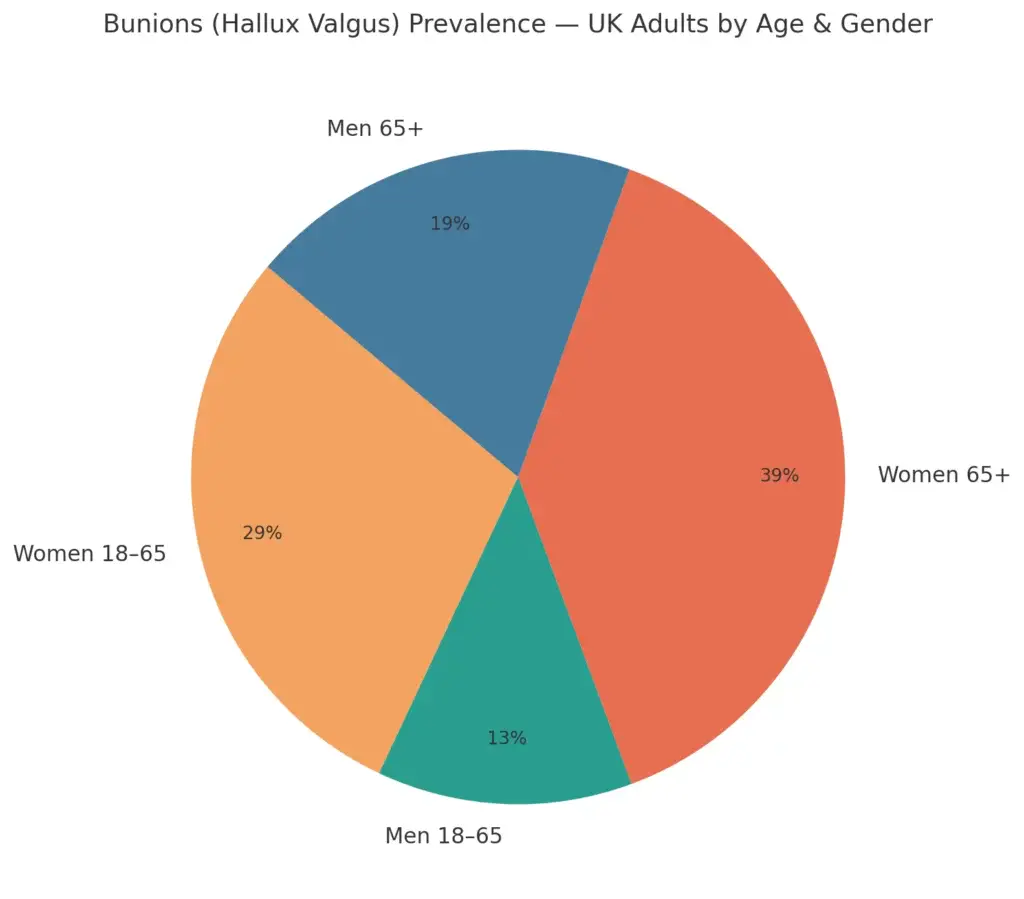
Estimated prevalence of bunions (hallux valgus) in UK adults, broken down by age and gender. Women are significantly more affected, particularly over 65.”
References
- Royal College of Podiatry – What are Bunions?
- NHS – Bunions Overview
- Nix S. et al. (2010). Prevalence of hallux valgus in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research
- Thomas M. et al. (2019). Population prevalence and associations of hallux valgus in older adults. BMJ Open
Prevalence figures are estimates drawn from systematic reviews and UK health sources. Women are significantly more affected than men, particularly over 65.
20 Common Bunion Questions
Q: Are bunions caused by wearing tight shoes?
A: Not directly, but tight or pointed shoes can make them worse if you’re already prone to bunions.
Q: Do bunions always get bigger?
A: They often worsen over time, though good footwear and orthotics can slow progression.
Q: Can bunions go away without surgery?
A: No. Conservative treatments relieve symptoms but don’t remove the bunion.
Q: What are the best shoes for bunions?
A: Wide-toe box shoes with soft uppers, cushioning, and adjustable fastenings.
Q: Are sandals good for bunions?
A: Yes — provided they have a wide footbed, cushioned soles, and supportive straps.
Q: Will losing weight help bunions?
A: It can reduce stress on the feet, easing pain, but won’t remove the bunion itself.
Q: Can bunions come back after surgery?
A: Yes, recurrence is possible if foot mechanics or footwear issues remain.
Q: Do toe spacers fix bunions?
A: They may provide temporary comfort but won’t correct the deformity.
Q: Is bunion pain worse in the morning?
A: Some people feel more stiffness and swelling after resting, especially if shoes aggravated them the day before.
Q: Can children get bunions?
A: Yes, bunions can appear in adolescence, often due to inherited foot mechanics.
Q: Should I buy bigger shoes for bunions?
A: Length isn’t the issue — choose wider shoes, not just longer ones.
Q: Can high heels cause bunions?
A: They can worsen them by pushing weight onto the forefoot and crowding toes.
Q: Are bunions linked to arthritis?
A: Yes. Bunions can form alongside or be aggravated by arthritis in the big toe joint.
Q: Do bunion splints work?
A: They may ease pain short-term but don’t correct the underlying joint alignment.
Q: Can men get bunions?
A: Absolutely — bunions affect both men and women, though they’re more common in women due to footwear trends.
Q: Do cushioned insoles help bunions?
A: Yes. They relieve pressure and improve comfort, especially during long days on your feet.
Q: How long does bunion recovery take after surgery?
A: Typically 6–12 weeks, though swelling can last several months.
Q: Can bunions cause balance problems?
A: Yes. As the toe shifts inward, it can affect foot stability.
Q: Are flip-flops bad for bunions?
A: Basic flat ones can be, but supportive sandals with arch support and cushioning are fine.
Q: Do wide-fit shoes prevent bunions?
A: They can reduce risk by minimising pressure and friction on the big toe joint.
📌 Summary
- Bunions are a structural foot condition worsened by poor footwear.
- The best shoes for bunions provide width, cushioning, and flexibility.
- At-home care, orthotics, and lifestyle changes relieve discomfort.
- Surgery is only for severe or unmanageable cases.

